
The main thing is to understand the difference between revert and reset. Now for the GUI question you had, you can prob right click on the commit you want to get back to ( reset) or remove the changes that one commit made ( revert) by right clicking a commit in the history tree or maybe theres a button to do it.

It is how developers and technical teams collaborate and work together on projects. this is DANGEROUS operation so be careful if you use it, you can change the state for other users of the repo. Dionysia Lemonaki Git is a powerful tool and the most popular version control system. you are changing the history of the project => when you perform git push you need to use the -force/ -f flag.
reset: you will move the state of your repository history back in time and possibly lose all the changes that were made on top of that. #GIT ROLLBACK LAST COMMIT HOW TO#
Let's look at how to roll back Git commits to a known-good version, as well as the implications and potential complications of doing so. Humans make mistakes, and consequently need to roll back to previous versions of content. you have not changed the history of the project but added to it => when you perform git push all is good Published: With Git, IT teams can implement version control. this means you create a new node in the commit tree, i.e.
revert: creates a new commit which is basically the opposite diff of the one created by the commit you are reverting (you'll see it in the automatic commit message). In this tutorial, we'll go through the most common commands to undo and revert commits in Git. Regarding the part where you asked to get back to a older state there are 2 ways: Introduction We often find ourselves needing to undo or revert a commit while using Git, whether it's to roll back to a particular point in time or revert a particularly troublesome commit. That is the way git keeps track of your changes (and you can check it with the log command, or in the GUI tree view of the history, not sure how its called since i dont use GUI for git) git folder in the repository and assigns a hash to that change. To answer your 1st question: after you run the commit command the file gets saved on your hard disk a s a normal file, but git also saves the diff of the change in the. Make sure you only use it to get rid of commits that haven't been pushed to another repository! This can cause some serious headaches if any of those lost commits have been pushed to a public repository. Ī note of warning that git reset will alter history - if I made several commits and then reset to the first commit, the subsequent commits will no longer be in the commit history. With the -hard option, it replaces the contents of your working directory with what was on. If you want to set your branch to the state of a particular commit (as implied by the OP), you can use git reset, or git reset -hard The first option only updates the INDEX, leaving files in your working directory unchanged as if you had made the edits but not yet committed them. It's more or less a way to 'undo' a commit and save that undo in your history as a new commit. 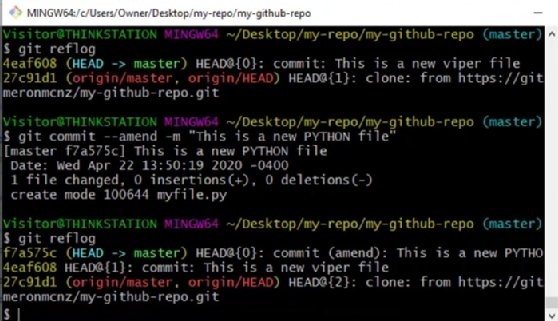
The above answer is not quite correct - git revert does not set your repository to that commit - git revert creates a new commit that undoes the changes introduced by commit.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
